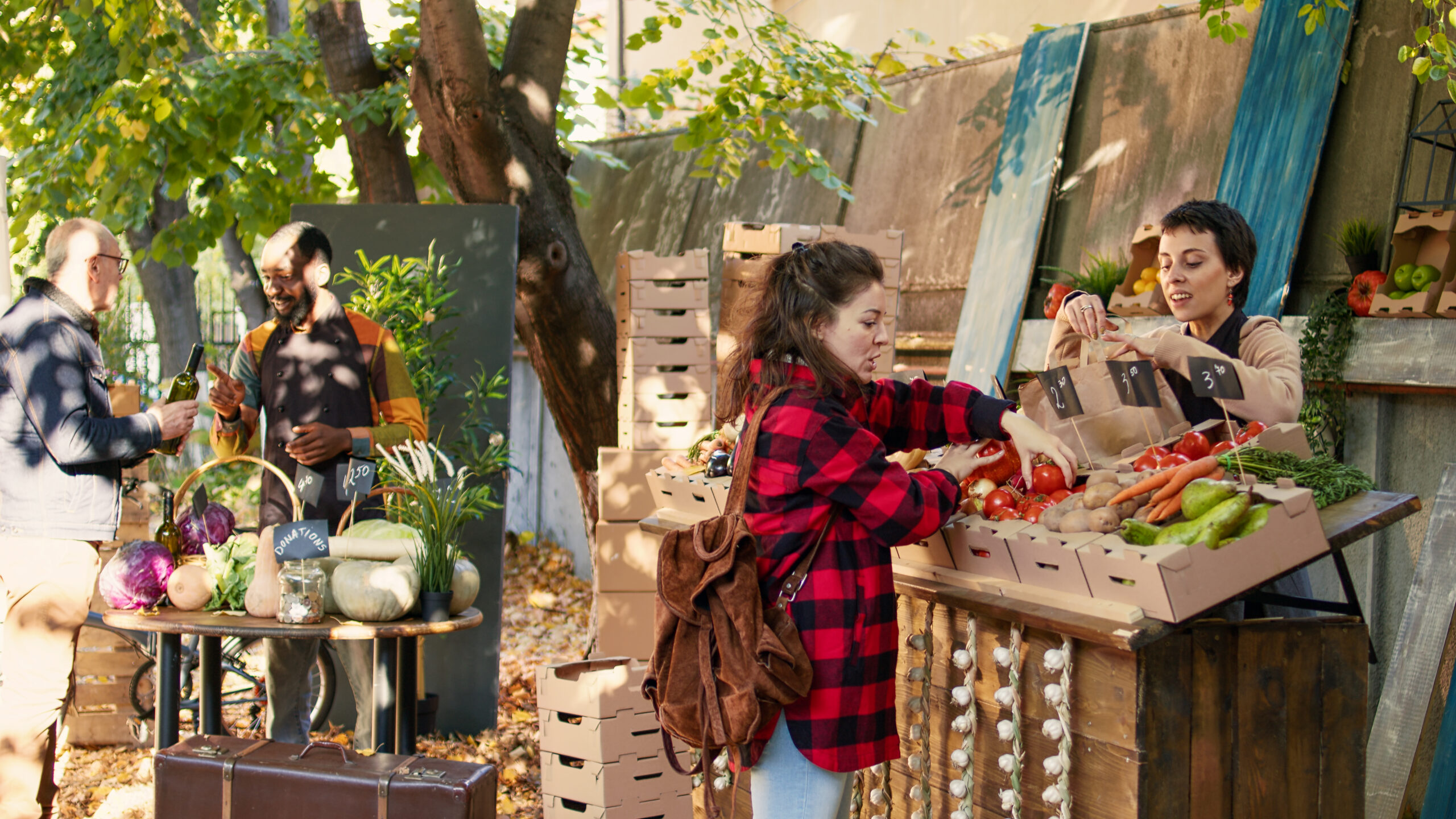

MARKET PLACE – LOCAL FOOD MARKET
Theme The students realize a presentation and tasting of local food products open to guests. Activity Duration 4 hours (in two different days) Group Size
We are excited to present you with an innovative tool specifically designed to enrich your work: a practical and dynamic Toolbox dedicated to integrating sustainability into learning contexts, through the application of non-formal learning methodologies.
The result of research on best practices in different areas of sustainability, this Toolbox will offer you a rich range of non-formal learning methods, accompanied by clear and concrete instructions for easy implementation in your daily activities.
The Toolbox is composed of different chapters that you can access according to the areas of your interest. The chapters collect the results of our project:
To use it, you can scroll through the Chapters in sequence or choose the chapter that interests you the most. Each chapter is linked to paragraphs and in-depth content.
All the contents of the Toolbox and the supporting materials will be available in four languages: English, Norwegian, Italian and Dutch.
This report shows the recommendations from the research done in the Sustainable Learning – Erasmus+ project; KA220-YOU – Cooperation Partnerships in Youth 2023 – 2026. Through our research, we have sought to shed light on the basic elements of the phenomenon of the “holistic learning process”. In order to do so, we have searched into the concepts of formal, non-formal and informal learning contexts.
This report is designed to support educators, teachers, and youth workers in transforming education systems to be more inclusive, sustainable, and future-oriented. It provides a comprehensive overview of key strategies and actionable recommendations for enhancing learning experiences. Topics include personalized education, sustainability integration, experiential learning, and non-formal learning validation. Through practical examples and guidance, this report aims to empower professionals in the education sector to implement meaningful, student-centered practices that address the diverse needs of today’s learners and prepare them for tomorrow’s challenges.
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is a dynamic classroom approach in which students actively explore real-world problems and challenges and acquire a deeper knowledge. PBL is a student-centered approach in which students learn by doing, working on a project over an extended period of time – from a week up to a semester – that engages them in investigating and responding to a complex question, problem, or challenge.
Key Components:
Driving Question:A compelling question that guides the project and sparks student curiosity.
Sustained Inquiry: An extended period of investigation, allowing students to delve deeply into the topic.
Authentic Context: Connecting the project to real-world issues and audiences.
Student Voice and Choice: Giving students opportunities to make decisions and personalize their learning.
Reflection and Revision: Encouraging students to reflect on their learning and revise their work based on feedback.
Public Presentation: Sharing the final product or findings with an audience beyond the classroom.
Benefits of PBL:
Increased student engagement and motivation.
Deeper understanding of content.
Development of essential 21st-century skills.
Enhanced critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Greater sense of ownership and responsibility for learning.
Key Components:
Benefits of PBL:
Place-Based Learning (PBL) is an educational approach that uses the local community and environment as the starting point to teach concepts in language arts, mathematics, social studies, science and other subjects across the curriculum. Emphasizing learning through participation in local projects, PBL encourages students to make real-world connections between their classroom learning and their wider community.
Key Principles:
Key Components:
Benefits of PBL:
Cooperative Learning is a teaching strategy in which small teams, each with students of different levels of ability, use a variety of learning activities to improve their understanding of a subject. Each member of a team is responsible not only for learning what is taught but also for helping teammates learn, thus creating an atmosphere of achievement.
Key Principles:
Key Components:
Benefits of Cooperative Learning:
Community Service Learning (CSL) is an educational approach that integrates meaningful community service with instruction and reflection. It aims to enrich the learning experience, teach civic responsibility, and strengthen communities. Students engage in activities that address community needs while applying academic skills and knowledge, fostering a deeper understanding of course content and its real-world applications.
Key Principles:
Key Components:
Benefits:
Problem-solving is a teaching method that focuses on developing students’ critical thinking and analytical skills by presenting them with real-world or simulated problems to solve. It encourages students to:
Key Principles:
Key Components:
Benefits of Problem-Solving:
Gamification is the application of game-design elements and game principles in non-game contexts. It aims to increase user engagement and motivation by incorporating elements such as:
Key Principles:
Key Components:
Benefits of Gamification:
Peer-to-peer (P2P) learning is an educational approach where individuals learn from and with each other, rather than solely from a designated instructor or expert. It emphasizes collaborative knowledge construction, mutual support, and shared responsibility for the learning process. This methodology leverages the diverse skills, experiences, and perspectives within a group to create a richer and more engaging learning environment. Here’s a breakdown of its key characteristics and how it typically works:
Key Principles:
Key components:
P2P learning can manifest in various forms, from informal study groups to structured pedagogical designs:
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Learning:
Read the full document to find out more about Non-Formal Learning
In the Sustainable Learning project, we believe education should unlock every young person’s potential. That means creating learning environments that are inclusive, adaptable, and meaningful—focusing not just on knowledge, but on the real skills young people need for life and the planet.
We identified two essential skill sets:
These skills are organised into a Skills Grid, each with clear, real-life abilities. For every skill, we’ve developed a rubric to track progress across five stages:
This framework supports both educators and learners, guiding personalised, future-ready learning paths.
The ability to continuously improve one’s self-awareness, emotional intelligence, and personal effectiveness. This involves setting goals, building confidence, managing emotions, developing resilience, and cultivating habits that lead to growth in both personal and professional life. It includes self-motivation, adaptability, time management, and a commitment to lifelong learning to achieve one’s full potential. The skills set of SL is not complete but within the topic of sustainability and NFL we have chosen the skills that are most important in this scope.
The ability to effectively exchange information, ideas, thoughts, and emotions through verbal, nonverbal, and written means. It involves not only expressing oneself clearly but also actively listening, understanding, and responding appropriately to others.
1. Verbal & Nonverbal Communication
Understand how to speak clearly, confidently, and at an appropriate pace.
Recognize how voice modulation and emotional expression impact messages.
Awareness of how posture, eye contact, and facial expressions convey meaning.
2. Active Listening & Understanding
Knowledge of how to focus, process, and respond to spoken messages.
Understanding how to ask questions and summarize information to ensure understanding.
Recognizing emotions and viewpoints in conversations to foster meaningful connections.
3. Written Communication
Mastery of language rules for clear and professional writing.
Understanding how to organize thoughts logically in writing.
Knowing appropriate ways to communicate via email, messaging, and social media.
4. Social & Interpersonal Communication
Understanding how to engage in balanced, meaningful discussions.
Recognizing different communication styles and respecting diverse viewpoints.
Learning how to handle disagreements constructively through communication.
5. Persuasion & Public Speaking
Knowledge of how to present ideas convincingly.
Understanding how to structure and deliver engaging speeches.
Techniques for reducing anxiety when speaking in front of others.
1. Verbal & Nonverbal Expression
The ability to speak clearly and pronounce words correctly.
The ability to adjust tone, volume, and pitch for effective delivery.
The ability to use appropriate facial expressions, gestures, and posture to enhance communication.
2. Active Listening & Understanding
The ability to fully engage in conversations without distractions.
The ability to understand spoken words, emotions, and underlying messages.
The ability to acknowledge and validate others’ perspectives.
3. Written Communication
The ability to construct well-formed sentences and use appropriate words.
The ability to structure thoughts logically in written form.
The ability to write appropriately for emails, texts, and social media.
4. Social & Interpersonal Abilities
The ability to engage in meaningful discussions and respond appropriately.
The ability to adjust communication style based on the audience and context.
The ability to handle disagreements constructively through communication.
5. Persuasion & Public Speaking
The ability to speak in front of groups without anxiety.
The ability to express opinions logically and persuasively.
The ability to capture and maintain an audience’s attention.
The ability to adapt to change, adjust to new situations, and remain open to different perspectives and approaches. It involves a willingness to modify plans, embrace uncertainty, and handle unexpected challenges with a positive mindset.
1. Adaptability & Change Management
Understanding Change – Recognizing that change is a natural and inevitable part of life.
Coping with Uncertainty – Learning how to stay calm and focused when things don’t go as planned.
Adjusting Plans – Knowing when and how to modify strategies to fit new circumstances.
2. Open-Mindedness & Perspective-Taking
Embracing New Ideas – Understanding that different approaches can lead to better solutions.
Appreciating Diverse Viewpoints – Recognizing the value of different opinions and cultural perspectives.
Constructive Feedback – Knowing how to receive and use feedback to improve.
3. Resilience & Emotional Regulation
Managing Stress & Frustration – Learning techniques to stay positive and composed under pressure.
Growth Mindset – Understanding that challenges and failures are opportunities for learning.
Confidence in Unfamiliar Situations – Knowing how to navigate new environments without fear.
4. Problem-Solving & Creative Thinking
Thinking on Your Feet – Understanding how to quickly adapt when unexpected challenges arise.
Creative Problem-Solving – Exploring multiple solutions when faced with obstacles.
Decision-Making Under Pressure – Knowing how to make thoughtful choices in uncertain situations.
5. Collaboration & Compromise
Balancing Personal Needs & Group Goals – Understanding when to be flexible to support teamwork.
Negotiation Skills – Knowing how to adjust expectations and find common ground.
Effective Communication – Understanding how to express adaptability while working with others.
1. Adaptability & Change Management
Ability to Adjust Quickly – Modify plans and behaviors when faced with unexpected changes.
Ability to Stay Composed – Maintain focus and avoid panic when dealing with uncertainty.
Ability to Reevaluate Strategies – Recognize when a new approach is needed and implement changes effectively.
2. Open-Mindedness & Perspective-Taking
Ability to Accept New Ideas – Consider different opinions and be willing to try new approaches.
Ability to Understand Others’ Perspectives – Actively listen and respect diverse viewpoints.
Ability to Apply Feedback – Use constructive criticism to improve performance and mindset.
3. Resilience & Emotional Regulation
Ability to Manage Emotions Under Pressure – Stay calm and positive when facing stress or setbacks.
Ability to Learn from Mistakes – View challenges as growth opportunities instead of failures.
Ability to Stay Confident in New Situations – Approach unfamiliar experiences with curiosity and self-assurance.
4. Problem-Solving & Creative Thinking
Ability to Think on Your Feet – Respond quickly and effectively to new challenges.
Ability to Adapt Solutions – Find alternative ways to overcome obstacles.
Ability to Make Decisions in Uncertain Situations – Weigh options and make sound judgments under pressure.
5. Collaboration & Compromise
Ability to Balance Individual and Group Needs – Adjust personal preferences to support teamwork.
Ability to Negotiate & Find Middle Ground – Work through conflicts and make fair compromises.
Ability to Communicate Adaptability – Express willingness to adjust in discussions and group efforts.
The ability to work effectively with others toward a shared goal by contributing ideas, actively listening, and respecting diverse perspectives. It involves communication, teamwork, adaptability, and problem-solving to achieve collective success.
1. Teamwork & Group Dynamics
Roles & Responsibilities – Understanding how different roles contribute to a group’s success.
Shared Goals & Objectives – Recognizing the importance of working toward common goals.
Interdependence – Knowing how individual contributions impact the entire group.
2. Communication & Active Listening
Clear Expression of Ideas – Understanding how to articulate thoughts respectfully and effectively.
Nonverbal Communication – Recognizing the role of body language, tone, and facial expressions in collaboration.
Active Listening Techniques – Knowing how to listen attentively, ask clarifying questions, and summarize key points.
3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving
Identifying Conflicts Early – Recognizing disagreements before they escalate.
Negotiation & Compromise – Understanding how to balance different viewpoints and find mutually beneficial solutions.
Constructive Feedback – Knowing how to give and receive criticism in a positive and helpful way.
4. Adaptability & Open-Mindedness
Embracing Diverse Perspectives – Understanding that different viewpoints can strengthen team outcomes.
Flexibility in Thinking – Knowing how to adjust ideas or strategies when necessary.
Resilience in Challenges – Recognizing that setbacks are part of teamwork and learning from them.
5. Accountability & Responsibility
Commitment to Tasks – Understanding the importance of meeting deadlines and fulfilling obligations.
Ownership of Mistakes – Recognizing and correcting errors rather than shifting blame.
Reliability in Group Work – Knowing that consistency builds trust and credibility within a team.
1. Teamwork & Group Participation
The ability to take on different roles within a group, whether as a leader, organizer, or contributor.
The ability to stay focused on shared objectives and work toward a common purpose.
The ability to actively participate, share ideas, and support others in a group setting.
2. Effective Communication & Active Listening
The ability to express ideas confidently, respectfully, and concisely.
The ability to interpret body language, tone, and facial expressions for better understanding.
The ability to listen attentively, ask clarifying questions, and summarize discussions to ensure mutual understanding.
3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving
The ability to manage emotions and stay calm during disagreements.
The ability to find fair compromises and resolve conflicts effectively.
The ability to give and receive criticism positively without defensiveness.
4. Adaptability & Open-Mindedness
The ability to understand and appreciate different viewpoints.
The ability to adjust strategies, plans, or approaches based on team needs.
The ability to learn from setbacks, remain optimistic, and stay motivated in group work.
5. Accountability & Reliability
The ability to take responsibility for assigned work and deliver on commitments.
The ability to admit mistakes and work toward solutions rather than shifting blame.
The ability to build trust by following through on responsibilities and being a reliable team member.
The ability to build and maintain positive relationships through effective communication, empathy, and consideration for others. It involves interacting respectfully, fostering trust, and showing compassion in personal and professional settings.
1. Emotional Intelligence
Understanding and managing your own emotions
Recognizing and responding to others’ emotions
Developing empathy and social awareness
2. Communication Skills
Verbal and non-verbal communication (tone, body language, facial expressions)
Active listening and responding appropriately
Clear and respectful articulation of thoughts
3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving
Identifying the root causes of conflicts
Using diplomacy and negotiation to resolve issues
Handling disagreements with patience and respect
4. Empathy & Perspective-Taking
Understanding different viewpoints and experiences
Practicing compassion and emotional support
Adapting communication to different personalities and needs
5. Social Etiquette & Professionalism
Respecting cultural and social norms
Understanding workplace dynamics and appropriate behavior
Building trust and credibility through honesty and integrity
6. Teamwork & Collaboration
Working effectively with diverse groups of people
Encouraging inclusivity and cooperation
Supporting and motivating others in group settings
7. Kindness & Positive Psychology
The psychological and social benefits of kindness
The impact of gratitude and small acts of kindness
Developing a mindset of generosity and appreciation
1. Emotional Intelligence
Ability to Recognize and Manage Emotions – Understand personal emotions and regulate reactions in different situations.
Ability to Interpret Others’ Emotions – Recognize emotional cues such as facial expressions, tone, and body language.
Ability to Show Emotional Awareness – Adjust behavior based on social and emotional contexts.
2. Communication Skills (Communication 1. Verbal & Nonverbal Expression, 2. Active Listening & Understanding)
Ability to Express Thoughts Clearly – Speak in a respectful and understandable way.
Ability to Use Effective Non-Verbal Communication – Maintain appropriate eye contact, tone, and gestures.
Ability to Actively Listen – Pay attention, ask questions, and respond appropriately.
3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving
Ability to Identify the Root Cause of Conflicts – Recognize underlying issues in disagreements.
Ability to Negotiate & Mediate Disputes – Find fair solutions while respecting all viewpoints.
Ability to Handle Disagreements with Patience – Stay calm, avoid escalation, and promote understanding.
4. Empathy & Perspective-Taking
Ability to Understand Others’ Feelings & Perspectives – See situations from another person’s point of view.
Ability to Offer Compassion & Emotional Support – Provide encouragement and kindness when others need it.
Ability to Adjust Communication for Different Personalities – Adapt interactions based on individual needs.
5. Social Etiquette & Professionalism
Ability to Respect Social & Cultural Norms – Behave appropriately in different social settings.
Ability to Maintain Professionalism – Follow proper etiquette in school, work, and formal environments.
Ability to Build Trust Through Honesty & Integrity – Act with sincerity and responsibility in relationships.
6. Teamwork & Collaboration (Collaboration: 1. Teamwork & Group Participation)
Ability to Work Well in Groups – Cooperate with peers, share responsibilities, and contribute positively.
Ability to Encourage Inclusivity & Fairness – Make sure everyone feels heard and valued.
Ability to Motivate & Support Others – Offer encouragement and recognize others’ efforts.
7. Kindness & Positive Psychology
Ability to Perform Acts of Kindness – Engage in small, meaningful gestures that help others.
Ability to Express Gratitude – Show appreciation for people’s efforts and support.
Ability to Cultivate a Generous Mindset – Offer help without expecting something in return.
The ability to work effectively with others toward a shared goal by contributing ideas, actively listening, and respecting diverse perspectives. It involves communication, teamwork, adaptability, and problem-solving to achieve collective success.
1. Emotional Intelligence
Understanding emotions (yours and others’)
Recognizing emotional triggers and managing reactions
Developing empathy and self-awareness
2. Self-Regulation Strategies
Stress management techniques (e.g., mindfulness, deep breathing)
Goal-setting and prioritization
Delayed gratification and impulse control
Maintaining focus and perseverance
3. Growth Mindset & Learning Attitude
Viewing feedback as a tool for improvement rather than criticism
Embracing challenges and learning from mistakes
Developing resilience and adaptability
4. Constructive Feedback Principles
Differentiating between constructive and destructive feedback
Understanding the intent behind feedback (help vs. criticism)
The role of feedback in professional and personal development
5. Active Listening & Communication
Practicing open-minded listening without defensiveness
Asking clarifying questions to fully understand feedback
Responding professionally and calmly
6. Behavioral Psychology & Habit Formation
Understanding how habits are formed and changed
Applying cognitive-behavioral techniques to regulate thoughts and emotions
Recognizing biases that affect how we perceive and accept feedback
1. Emotional Control & Self-Discipline
Managing impulses and emotions in challenging situations
Staying calm under pressure and avoiding reactive behavior
Demonstrating patience and resilience
2. Self-Awareness & Reflection
Recognizing personal strengths and areas for improvement
Identifying emotional triggers and biases
Engaging in regular self-assessment and reflection
3. Openness to Feedback & Growth
Actively listening without becoming defensive
Accepting criticism as an opportunity to improve
Distinguishing between constructive and unhelpful feedback
4. Adaptability & Flexibility ( Flexibility: 1. Adaptability & Change Management)
Adjusting behavior and mindset based on feedback
Embracing change and new perspectives
Handling unexpected situations with a problem-solving attitude
5. Active Listening & Communication ( Communication: 2. Active Listening & Understanding)
Fully concentrating on what is being said before responding
Asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding
Expressing appreciation for feedback, even when it’s difficult to hear
6. Goal-Setting & Self-Motivation
Setting clear, realistic personal and professional goals
Maintaining focus on long-term objectives despite setbacks
Tracking progress and making adjustments based on feedback
7. Stress Management & Resilience ( Flexibility: 3. Resilience & Emotional Regulation)
Developing coping strategies for dealing with setbacks
Bouncing back from criticism or failure with a positive attitude
Maintaining confidence and motivation despite challenges
The ability to take proactive action, independently recognize opportunities, and drive tasks or goals forward without needing external direction. It involves self-motivation, resourcefulness, and a willingness to take responsibility for making things happen.
1. Self-Knowledge
Personal Strengths & Weaknesses – Understanding one’s capabilities, limitations, and areas for growth to take proactive steps.
Motivation & Goal-Setting – Knowledge of what drives personal and professional ambitions.
Growth Mindset – Recognizing that skills and abilities can be developed through effort and persistence.
2. Problem-Solving & Decision-Making Knowledge
Critical Thinking – The ability to analyze situations and make informed decisions.
Risk Assessment – Knowing how to evaluate potential risks and rewards before taking action.
Strategic Planning – Understanding how to set clear goals and develop step-by-step approaches to achieve them.
3. Professional & Industry-Specific Knowledge
Field Expertise – Mastery of relevant industry trends, best practices, and innovations.
Business & Market Awareness – Understanding how organizations operate and how to identify growth opportunities.
Resource Management – Knowledge of how to leverage available resources effectively to achieve goals.
4. Communication & Social Knowledge
Interpersonal & Networking Skills – Understanding how to build relationships, collaborate, and influence others.
Persuasion & Negotiation – Knowledge of how to advocate for ideas and gain support.
Team Dynamics – Awareness of how to contribute to and lead teams effectively.
5. Time & Productivity Management
Prioritization Techniques – Understanding how to focus on high-impact tasks.
Self-Discipline & Organization – Knowing how to manage workloads without external pressure.
Resilience & Stress Management – Awareness of strategies to stay persistent and motivated despite challenges.
1. Self-Starting & Proactiveness
Taking Action Without Being Told – The ability to recognize what needs to be done and act without waiting for instructions.
Recognizing Opportunities – The ability to spot areas for improvement, innovation, or growth.
Anticipating Challenges – The foresight to address problems before they arise.
2. Decision-Making & Problem-Solving (Collaboration 3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving)
Critical Thinking – The ability to assess situations and determine the best course of action.
Risk-Taking & Risk Management – Confidence in making decisions despite uncertainty while balancing risks and rewards.
Adaptability & Flexibility – The ability to adjust strategies when faced with new challenges or information.
3. Self-Management & Discipline
Self-Motivation – The internal drive to set and achieve goals without external pressure.
Time Management – Prioritizing tasks efficiently to stay productive and proactive.
Resilience & Persistence – Overcoming obstacles, setbacks, and failures with determination.
4. Communication & Social Influence
Persuasion & Negotiation – The ability to convince others and gain support for ideas.
Collaboration & Leadership – Taking charge when necessary while working effectively with others.
Confidence & Assertiveness – Expressing ideas and taking initiative in group settings.
5. Creativity & Innovation
Thinking Outside the Box – The ability to develop new ideas and approaches.
Experimentation & Learning from Failure – Willingness to test new strategies and learn from mistakes.
Resourcefulness – Finding solutions even with limited resources or guidance.
the ability to innovate, take initiative, and transform ideas into reality by identifying opportunities, solving problems, and taking calculated risks. These skills involve creativity, leadership, adaptability, and resourcefulness in developing new projects, businesses, or solutions.
1. Innovation & Creative Thinking
Understanding Innovation – The role of new ideas in solving problems and creating value.
Creative Problem-Solving Techniques – Brainstorming, lateral thinking, and design thinking.
Opportunity Recognition – Identifying gaps in the market or areas for improvement.
2. Initiative & Risk-Taking
Self-Motivation & Proactiveness – Taking action without waiting for instructions.
Risk Assessment – Evaluating potential risks and rewards before making decisions.
Decision-Making Under Uncertainty – Making informed choices despite incomplete information.
3. Problem-Solving & Adaptability
Resilience & Overcoming Challenges – Learning from failures and setbacks.
Flexibility in Changing Circumstances – Adapting strategies based on new information.
Critical Thinking & Logical Reasoning – Analyzing problems and finding the best solutions.
4. Leadership & Collaboration
Vision & Goal-Setting – Defining objectives and creating a roadmap to success.
Teamwork & Delegation – Working effectively with others and assigning tasks strategically.
Influencing & Persuasion – Communicating ideas convincingly to gain support.
5. Business & Financial Literacy
Basic Entrepreneurship Principles – Understanding business models, supply and demand, and value creation.
Financial Management – Budgeting, managing expenses, and understanding profitability.
Marketing & Branding – Promoting ideas, products, or projects to the right audience.
6. Resourcefulness & Networking
Utilizing Available Resources – Making the most of skills, tools, and opportunities.
Building Connections & Partnerships – Networking with mentors, investors, or team members.
Resilience in Uncertain Situations – Finding creative solutions when resources are limited.
1. Self-Starting & Proactiveness
Taking Action Without Being Told – The ability to recognize what needs to be done and act without waiting for instructions.
Recognizing Opportunities – The ability to spot areas for improvement, innovation, or growth.
Anticipating Challenges – The foresight to address problems before they arise.
2. Decision-Making & Problem-Solving (Collaboration 3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving)
Critical Thinking – The ability to assess situations and determine the best course of action.
Risk-Taking & Risk Management – Confidence in making decisions despite uncertainty while balancing risks and rewards.
Adaptability & Flexibility – The ability to adjust strategies when faced with new challenges or information.
3. Self-Management & Discipline
Self-Motivation – The internal drive to set and achieve goals without external pressure.
Time Management – Prioritizing tasks efficiently to stay productive and proactive.
Resilience & Persistence – Overcoming obstacles, setbacks, and failures with determination.
4. Communication & Social Influence
Persuasion & Negotiation – The ability to convince others and gain support for ideas.
Collaboration & Leadership – Taking charge when necessary while working effectively with others.
Confidence & Assertiveness – Expressing ideas and taking initiative in group settings.
5. Creativity & Innovation
Thinking Outside the Box – The ability to develop new ideas and approaches.
Experimentation & Learning from Failure – Willingness to test new strategies and learn from mistakes.
Resourcefulness – Finding solutions even with limited resources or guidance.
The ability to inspire, guide, and influence others toward achieving a common goal. It involves decision-making, communication, problem-solving, and the ability to motivate and support a team while demonstrating responsibility and integrity.
1. Self-Awareness & Personal Development
Understanding Strengths & Weaknesses – Recognizing personal abilities and areas for improvement.
Confidence & Self-Efficacy – Developing belief in one’s ability to lead and influence others.
Growth Mindset – Embracing challenges as opportunities for learning and self-improvement.
2. Communication & Influence
Clear & Persuasive Communication – Knowing how to express ideas confidently and effectively.
Active Listening – Understanding the importance of listening to others’ ideas, concerns, and feedback.
Nonverbal Communication – Recognizing how body language, eye contact, and tone of voice impact leadership.
3. Decision-Making & Problem-Solving
Critical Thinking & Analysis – Understanding how to evaluate information objectively and make informed decisions.
Risk Assessment – Recognizing potential risks and making calculated choices.
Adaptability in Decision-Making – Knowing when to adjust strategies based on new information.
4. Teamwork & Collaboration
Delegation & Trust – Understanding how to assign tasks effectively and trust team members.
Conflict Resolution – Recognizing how to mediate disagreements and create win-win solutions.
Encouraging Inclusivity – Knowing how to promote diverse perspectives and create a positive team environment.
5. Motivation & Inspiration
Leading by Example – Understanding the impact of personal actions and behavior on a team.
Encouraging & Supporting Others – Knowing how to inspire motivation and build team morale.
Providing Constructive Feedback – Recognizing how to guide and mentor others through supportive criticism.
6. Responsibility & Ethical Leadership
Accountability for Actions – Understanding the importance of taking responsibility for decisions and outcomes.
Integrity & Honesty – Recognizing the role of ethical decision-making in leadership.
Commitment & Perseverance – Knowing how to stay dedicated to goals despite challenges.
1. Develop Self-Awareness & Personal Growth (Apply self regulation & accept feedback: 2. Self-Awareness & Reflection 3. Openness to Feedback & Growth)
Ability to reflect on strengths and weaknesses through journaling or self-assessments.
Ability to set personal and leadership goals for improvement. Ability to step out of comfort zones by taking on new challenges.
2. Strengthen Communication & Influence
Ability to practice speaking confidently in group discussions and presentations.
Ability to listen actively by making eye contact, asking clarifying questions, and summarizing key points.
Ability to use body language effectively to show confidence and engagement.
3. Improve Decision-Making & Problem-Solving
Ability to analyze situations critically before making choices.
Ability to take calculated risks and reflect on outcomes.
Ability to adapt plans based on new information and unexpected challenges.
4. Enhance Teamwork & Collaboration
Ability to assign tasks to team members based on their strengths and trust their abilities.
Ability to mediate conflicts by listening to different perspectives and suggesting solutions.
Ability to foster inclusivity by ensuring everyone’s voice is heard and valued.
5. Inspire & Motivate Others
Ability to lead by example with a positive attitude and strong work ethic.
Ability to recognize and celebrate others’ achievements.
Ability to offer constructive feedback to help peers grow and improve.
6. Demonstrate Responsibility & Ethical Leadership
Ability to take ownership of successes and mistakes instead of blaming others.
Ability to act with honesty and integrity, making ethical choices even when difficult.
Ability to show persistence and commitment to long-term goals, even in the face of setbacks.
The ability to analyze, evaluate, and interpret information objectively in order to make reasoned decisions and solve problems effectively. It involves questioning assumptions, recognizing biases, assessing evidence, and thinking logically to arrive at well-founded conclusions.
1. Logical Thinking & Reasoning
Understanding deductive (general to specific) and inductive (specific to general) reasoning.
Recognizing how actions lead to consequences.
Identifying flawed arguments such as circular reasoning, false dilemmas, and ad hominem attacks.
2. Problem-Solving & Decision-Making
Techniques like breaking problems into smaller parts and identifying key issues.
Knowledge of frameworks like cost-benefit analysis, pros-and-cons lists, and evidence-based decision-making.
Understanding multiple perspectives and possible solutions before making conclusions.
3. Evaluation of Information & Evidence
Recognizing the difference between objective facts and subjective viewpoints.
Assessing whether information comes from reliable and unbiased sources.
Understanding how personal, cultural, or media biases influence thinking and decision-making.
4. Questioning & Inquiry
Learning how to ask deep, open-ended questions to challenge assumptions.
Encouraging a habit of seeking knowledge and asking “why” or “how.”
Understanding how preconceived ideas influence opinions and judgments.
5. Reflection & Self-Awareness
Awareness of one’s own thought processes and how they impact decision-making.
Recognizing how emotions can cloud judgment and affect reasoning.
The ability to assess one’s own biases and thought patterns objectively.
1. Logical Thinking & Reasoning
The ability to break down complex information into smaller, understandable parts.
The ability to draw conclusions based on evidence and sound reasoning.
The ability to identify trends, connections, and inconsistencies in information.
2. Problem-Solving & Decision-Making(Collaboration 3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving)
The ability to form personal judgments instead of relying solely on others’ opinions.
The ability to evaluate different viewpoints before making a decision.
The ability to foresee the potential outcomes of choices.
3. Information Evaluation & Objectivity
The ability to assess the credibility of information and identify misinformation.
The ability to detect biases in media, arguments, and personal beliefs.
The ability to separate emotions from logical analysis.
4. Questioning & Inquiry
The ability to ask deep, thoughtful questions and remain receptive to new ideas.
The ability to challenge assumptions by asking “Why?”, “How?”, and “What if?”
The ability to define problems clearly before attempting to solve them.
5. Reflection & Self-Awareness ( Apply self regulation & accept feedback: 2. self awareness and reflection)
The ability to think about one’s own thinking and reasoning processes.
The ability to manage emotions so they don’t cloud judgment.
The ability to adjust beliefs or opinions when presented with new, credible evidence.
The ability to access, analyze, evaluate, create, and responsibly use different forms of media. It involves understanding how media messages are constructed, recognizing bias and misinformation, and using media effectively for communication and expression.
1. Understanding Different Types of Media
Recognizing the format and purpose of various media (inform, entertain, persuade, etc.).
2. Identifying Bias & Misinformation
Methodology to fact-check and recognize fake news or misleading information
3. Digital Citizenship & Ethical Use of Media
Principles to use media responsibly and respectfully.
Issues like cyberbullying, privacy, and online safety.
4. Media Production & Content Creation
Criteria to create responsible and ethical media content (videos, blogs, social media posts, etc.).
Copyright laws, digital footprints, and responsible sharing.
5. Critical Thinking & Media Influence Awareness
Advertising tactics, propaganda, and persuasive techniques.
1. Media Analysis & Interpretation
The ability to recognize different types of media (news, entertainment, advertisements, social media, etc.) and their purposes.
The ability to assess the accuracy, reliability, and intent behind media messages.
The ability to understand how culture, politics, and business influence media content.
2. Bias & Misinformation Detection (Critical thinking: 3. Information Evaluation & Objectivity)
The ability to verify claims by cross-referencing credible sources.
The ability to detect and evaluate biases in news, social media, and advertisements.
The ability to recognize fake news, deepfakes, and manipulated media.
3. Digital Citizenship & Ethical Media Use
The ability to engage respectfully and safely in digital spaces.
The ability to protect personal information and understand data tracking.
The ability to recognize, prevent, and address online harassment.
4. Media Production & Content Creation
The ability to create engaging and responsible media content.
The ability to respect intellectual property and use media legally.
The ability to manage one’s online presence responsibly.
5. Critical Thinking & Media Influence Awareness
The ability to recognize marketing strategies, propaganda, and persuasive techniques.
The ability to critically assess how media influences opinions, behaviors, and purchasing decisions.
The ability to form well-reasoned opinions rather than being passively influenced by media.
Practical and technical hard skills in the context of sustainability refer to the specific abilities and knowledge needed to implement sustainable practices and solutions. These skills are often tangible and measurable, and they enable individuals to directly contribute to environmental protection and resource conservation.
To apply five principles of zero waste consisting of: Reuse, Reduce, Recycle, Refuse and Compost with the general objective and reference to achieve zero waste. Zero waste means to the conservation of all resources by means of responsible production, consumption, reuse, and recovery of products, packaging, and materials without burning and with no discharges to land, water, or air that threaten the environment or human health.
1. Waste Streams: Understanding the different types of waste (organic, recyclable, hazardous, etc.) and where they come from.
2. Environmental Impact: Awareness of the negative effects of waste on ecosystems, climate change, and human health.
3. Waste Reduction Strategies: Knowledge of the “5 R’s” (Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose, Recycle) and other methods for minimizing waste.
4. Composting: Understanding the composting process, materials, and how to create nutrient-rich soil.
5. Recycling Systems:Knowledge of local recycling guidelines, materials accepted, and how to properly prepare items.
6: Sustainable Products: Familiarity with eco-friendly alternatives to common household items and packaging.
Understanding the concept of designing systems where resources are continuously reused and waste is minimized.
1. Waste Auditing: Analyzing one’s own waste generation to identify areas for improvement.
2. Conscious Consumption: Making informed purchasing decisions, avoiding single-use items and excessive packaging.
3. Creative Reuse: Finding new purposes for items that would otherwise be discarded.
Repair and Maintenance: Extending the lifespan of products by repairing them instead of replacing them.
4. Composting: Setting up and maintaining a compost system.
Recycling: Sorting and properly preparing materials for recycling.
5. Advocacy: Encouraging others to reduce waste and supporting businesses with sustainable practices.
Additional Considerations:
Context:The specific knowledge and abilities needed may vary depending on the setting (home, workplace, community).
This skill is about efficiently harnessing and utilizing energy resources within a system. It involves recognizing, capturing, and storing various forms of energy for later use.
1. Energy Sources: Understanding different types of energy (solar, wind, water, biomass, etc.) and their characteristics.
2. Energy Flow: Knowledge of how energy moves through systems and how to maximize its capture and minimize losses.
3. Storage Methods: Familiarity with various energy storage techniques (batteries, thermal mass, water reservoirs, etc.) and their applications.
4. System Design: Understanding how to integrate energy capture and storage into the design of a system (e.g., building, garden, or ecosystem).
5. Resource Management: Knowledge of sustainable resource management practices and their impact on energy efficiency.
1. Ability to evaluate energy availability and needs within a system.
2. Ability to implement methods to capture energy from various sources (e.g., solar panels, rainwater harvesting, composting).
3. Ability to select and implement appropriate energy storage solutions based on the specific context.
4. Ability to design and optimize systems to maximize energy efficiency and minimize waste.
5. Ability to monitor energy use and storage, and make adjustments as needed to improve performance.
This skill is about efficiently harnessing and utilizing energy resources within a system. It involves recognizing, capturing, and storing various forms of energy for later use.
1. Resource Assessment: Ability to evaluate the availability and potential of renewable resources in a given area.
2. Utilization Techniques: Ability to apply methods to harness renewable resources (e.g., installing solar panels, composting, using public transportation).
3. Conservation Practices: Ability to adopt practices that reduce consumption and minimize waste, thereby preserving resources.
4. Advocacy and Education: Ability to promote the use of renewable resources and educating others about their importance.
5. Value Recognition: Ability to appreciate the intrinsic value of renewable resources and the services they provide to sustain life.
This competence focuses on the cognitive benefits of neurodiversity, highlighting the unique perspectives and problem-solving approaches that individuals with neurological differences can bring.This competence emphasizes the value of neurodiversity in fostering a more inclusive and innovative environment. It recognizes that individuals with neurological differences possess unique cognitive strengths that can be harnessed to enhance problem-solving, creativity, and overall success.
1. Concept of Neurodiversity: A solid grasp of the concept of neurodiversity, including the various neurological differences (e.g., autism, ADHD, dyslexia) and their associated strengths and challenges.
2. Cognitive Differences: Knowledge of how different neurological profiles can lead to variations in thinking styles, information processing, and problem-solving approaches.
3. Benefits of Diverse Thinking: Awareness of the advantages of incorporating diverse perspectives in decision-making, innovation, and problem-solving.
4. Potential Challenges: Understanding the potential challenges faced by neurodivergent individuals in traditional work environments and the accommodations that can support their success.
1. Diverse Thinking: ( Initiative: 5. Creativity & Innovation)Ability to think in unique and unconventional ways, often leading to creative solutions and innovative ideas.
2. Pattern Recognition: Ability to identify patterns, connections, and insights that might be missed by neurotypical individuals.
3. Systems Thinking: Ability to analyze situations holistically, considering the interconnectedness of various elements.
4. Problem-Solving: Interpersonal skill and kindness: 3. Conflict Resolution & Problem-Solving )Ability to approach problemsfrom multiple angles, leveraging unique perspectives and cognitive strengths.
Adaptability: Flexibility: 1. Adaptability & Change Management)Ability to adjust thinking and approaches based on new information or changing circumstances.
5. Communication: (Communication 1. Verbal & Nonverbal Expression, 2. Active Listening & Understanding) Ability to effectively communicate ideas and perspectives, even if they differ from conventional thinking.
6. Collaboration Interpersonal skills and kindness: 6. Teamwork & Collaboration (Collaboration: 1. Teamwork & Group Participation): Ability to work effectively with others, leveraging diverse thinking styles to achieve shared goals.
The skill emphasizes a deliberate and incremental approach, often prioritizing long-term sustainability and resilience over quick fixes. It’s about understanding the value of gradual progress and avoiding the pitfalls of rushed or overly ambitious solutions. In essence, this competence is about valuing a thoughtful, measured approach that prioritizes long-term success and resilience over the allure of quick fixes. It’s about understanding that sometimes, the slowest path is the most direct route to sustainable and meaningful change.
1. Systems Thinking: Understanding how interconnected parts of a system can be affected by interventions, recognizing that quick fixes can have unintended consequences elsewhere. Knowing that complex problems often require nuanced, gradual solutions.
Sustainability Principles: Awareness of the long-term impacts of decisions, considering environmental, social, and economic factors. Understanding that “small and slow” often aligns with sustainable practices.
2. Risk Management: Knowledge of how to assess and mitigate risks, recognizing that rapid changes can introduce unforeseen dangers. Understanding that a slow, measured approach allows for better risk assessment and adaptation.
3. Change Management: Understanding the psychology of change and how gradual implementation can facilitate smoother transitions and better adoption. Knowing that people often resist sudden, drastic changes.
4. Lean Principles: Familiarity with the concept of minimizing waste and maximizing value through incremental improvements. Understanding how “small and slow” can lead to efficiency gains over time.
Complexity Theory: Awareness that complex systems are often unpredictable and that trying to impose large-scale solutions can lead to unintended consequences. Understanding that iterative, adaptive approaches are often more effective.
1. Patience & Perseverance: Ability to stick with a problem and implement solutions gradually, even when progress seems slow. Resisting the urge for immediate gratification.
2. Incrementalism: ability to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps and implement solutions incrementally.
3. Adaptability & Interation: ability to monitor progress, learn from mistakes, and adjust solutions as needed. Embracing the iterative nature of problem-solving.
4. Observation & Analysis: ability to carefully observe and analyze the effects of small changes before implementing larger ones. Paying attention to detail.
5. Long-Term Thinking: ability to consider the long-term consequences of decisions and prioritize sustainability over short-term gains.
6. Resilience: ability to bounce back from setbacks and continue working towards long-term goals, even in the face of challenges.
7. Communication & Collaboration: (Collaboration: 1. Teamwork and group participation) ability to effectively communicate the rationale for a “small and slow” approach and build consensus among stakeholders. Explaining the benefits of gradual progress.
The Sustainable Learning project has developed a database of examples of Learning Activities involving the use of non-formal learning methodologies. The database is structured on the basis of the project’s Skillsgrid. The threads allows activities to be selected on the basis of the target skills and methodologies used. Some learning activities can be linked together in modular form in order to compose longer and more structured learning paths. In the database of Learning Activities you can find the description of the activities, necessary tools, the objectives and the steps necessary to achieve them.
Read the full document to find out more about Sustainability and Learning

Theme The students realize a presentation and tasting of local food products open to guests. Activity Duration 4 hours (in two different days) Group Size
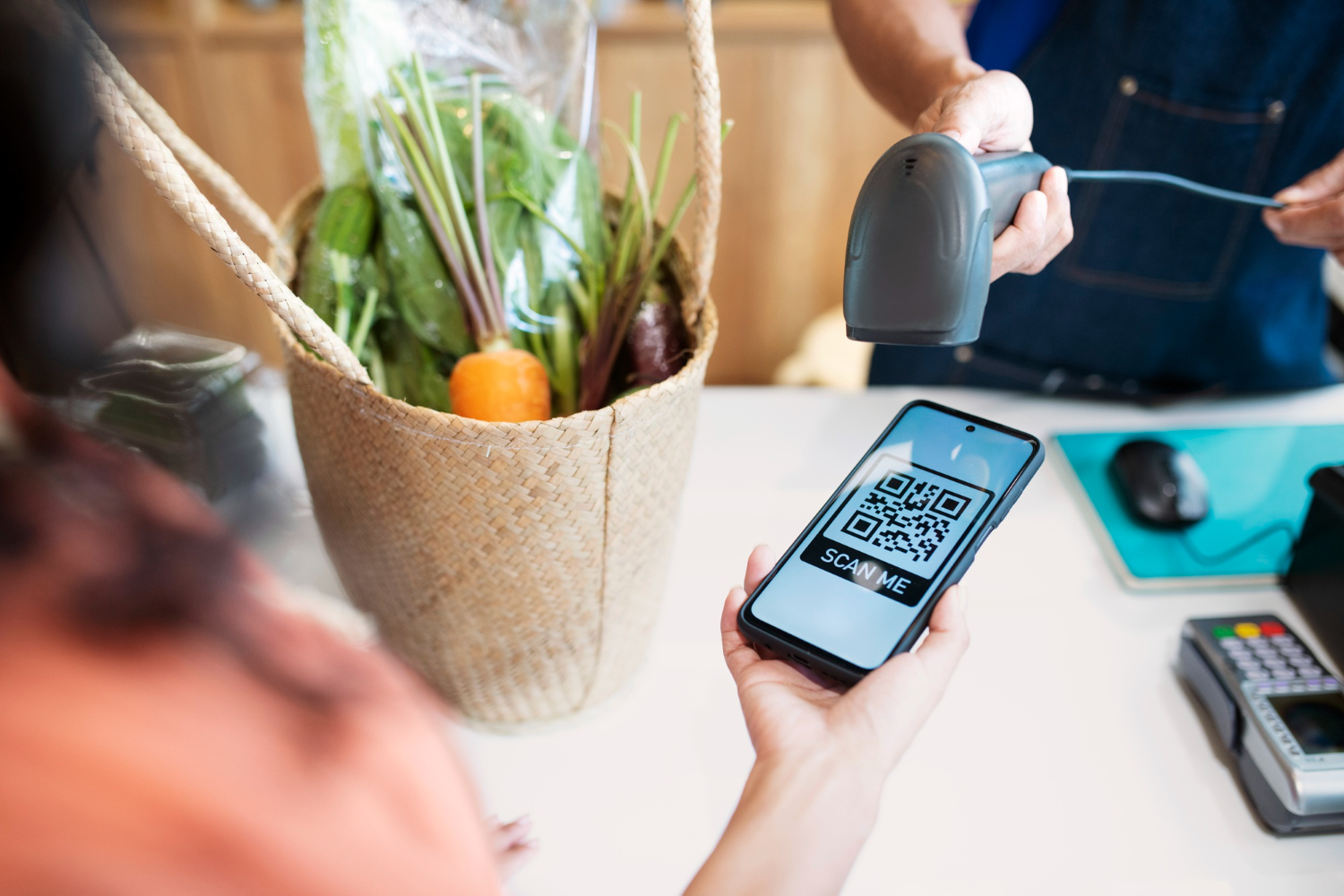

Theme The students realize digital tools to enhance the value of local food products. Activity Duration 6 hours Group Size 12-20 youngsters Objectives Develop knowledge
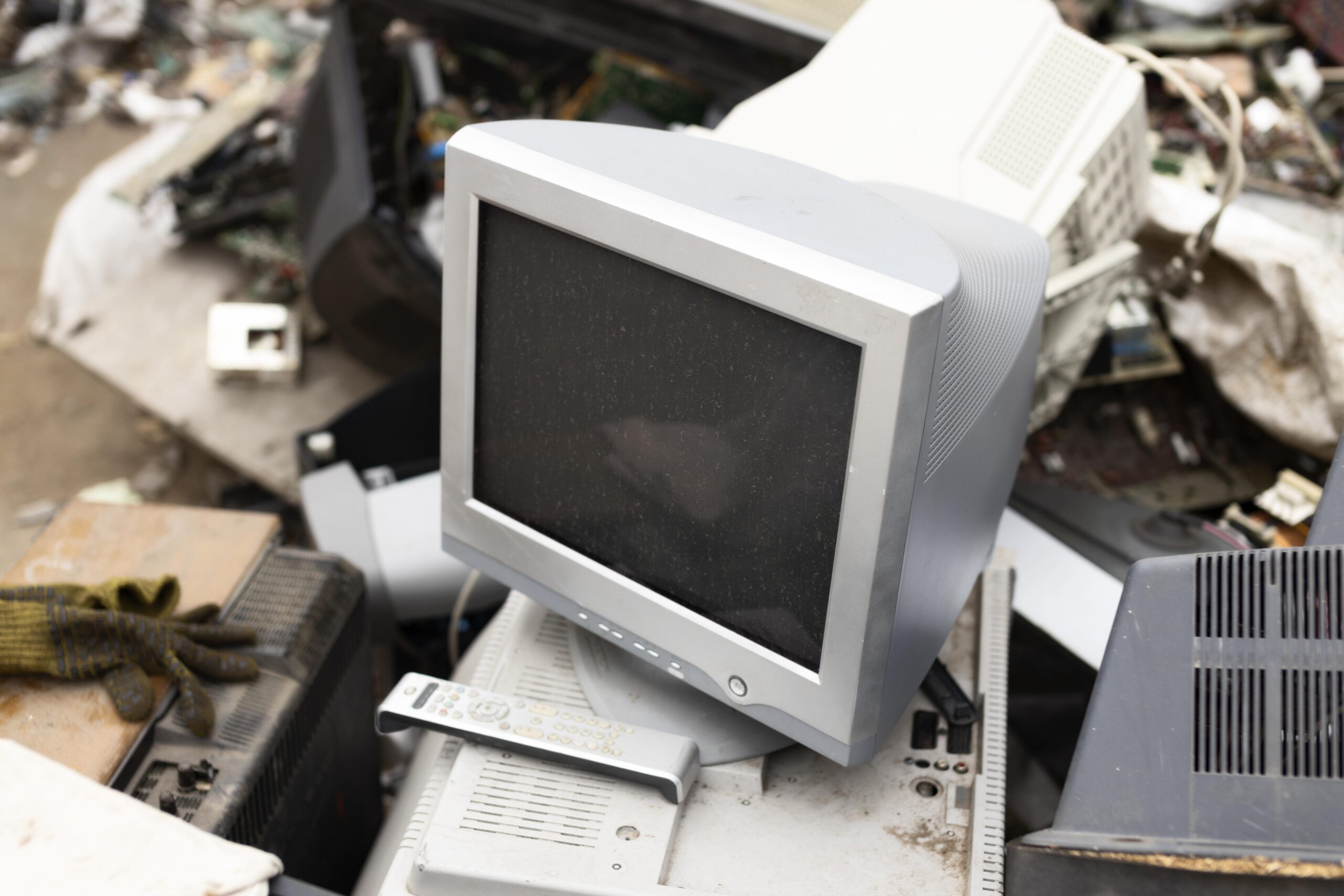

Theme Restoring and reselling used laptops. Activity Duration 2 – 3 hours Group Size 2-3 youngsters Objectives Use principles for troubleshooting and correction when working
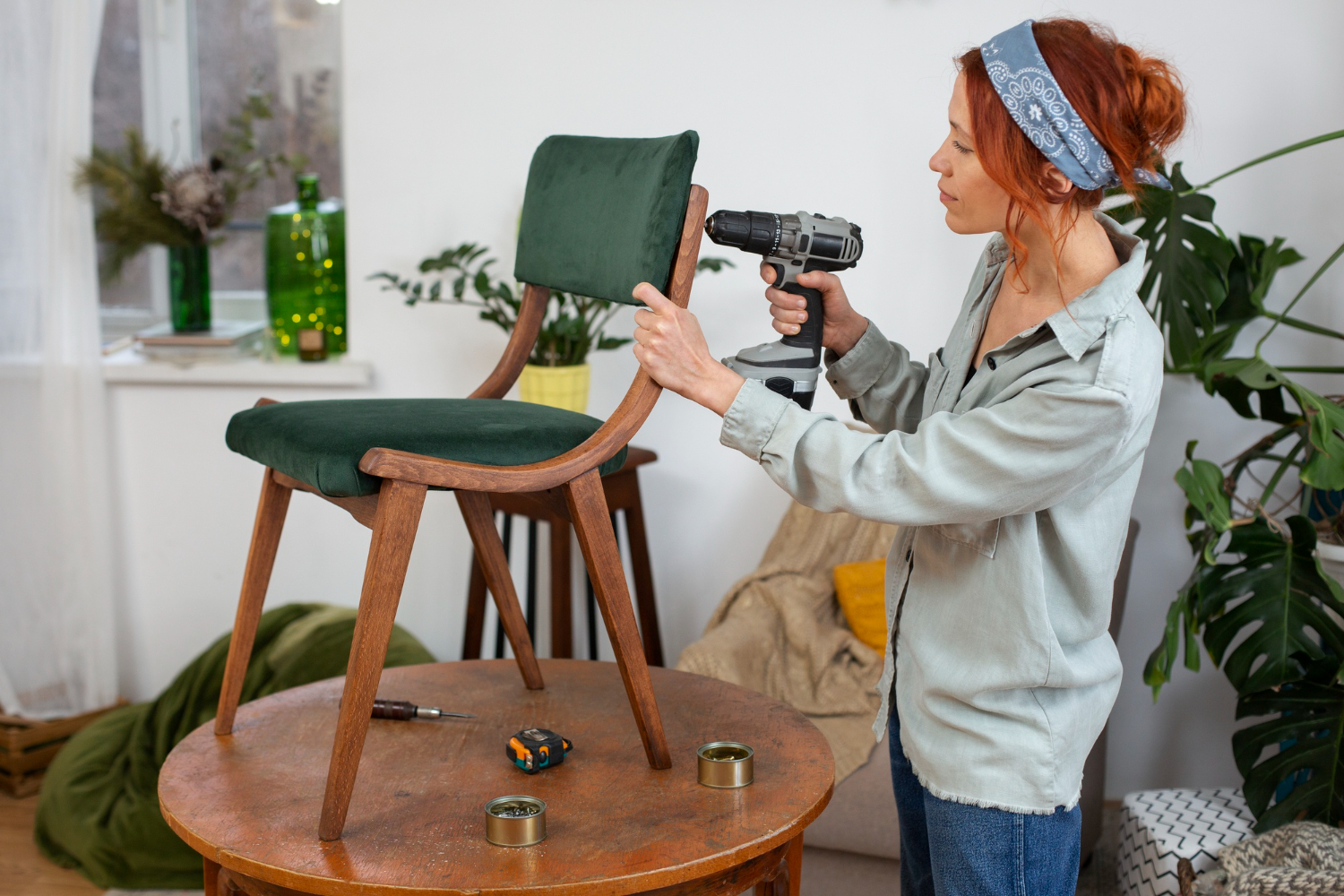

Theme Repairingring and renovating lift chair for the communituy technical aid service. Activity Duration 3-5 hours depending on tecknical skillset. Group Size 2-3 youth Objectives
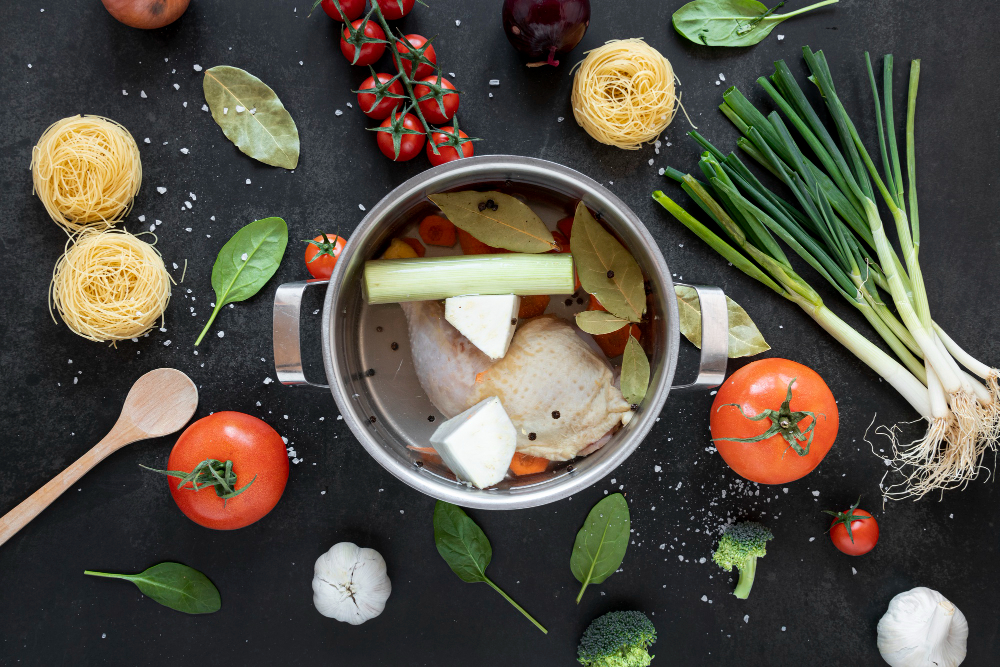

Theme Making soup of residual products Activity Duration 3 hours Group Size 15 – 25 youth Objectives preventing food waste students learn how to prevent
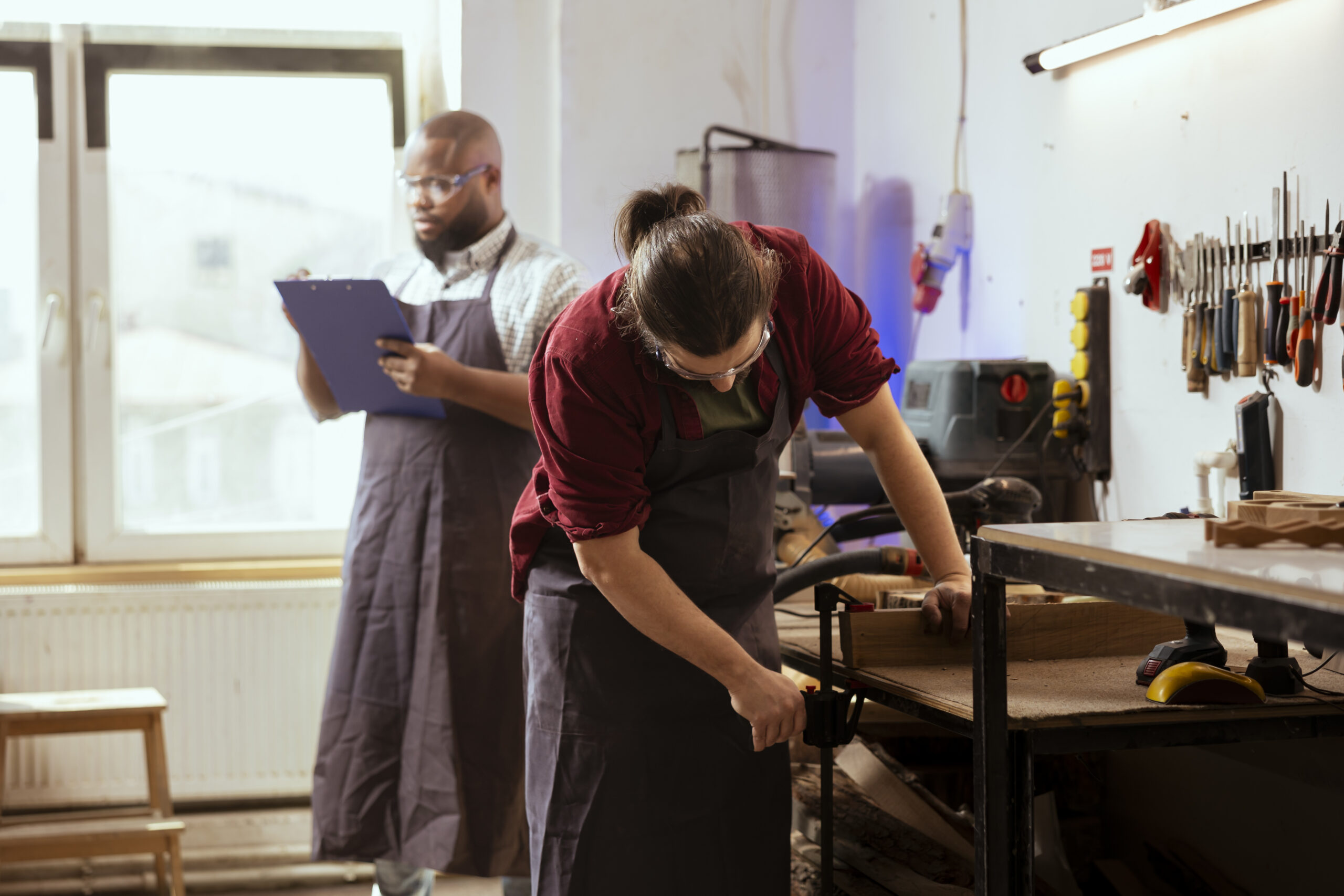

Theme Repairing electrical (household) appliances with peers for the community Activity Duration 4 – 8 hours Group Size 5 – 10 students Objectives Practical skills:
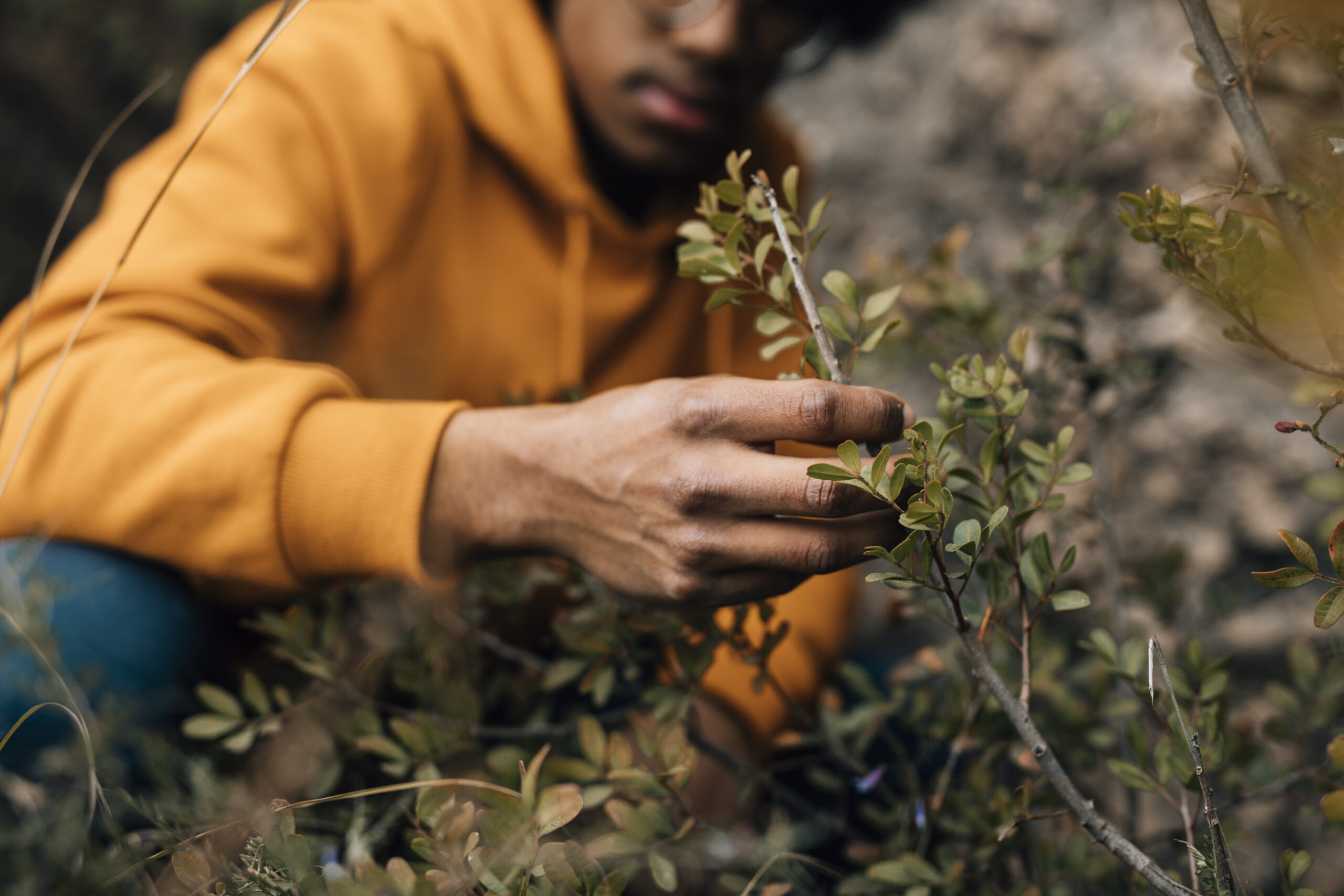

Theme Knowledge and valorization of edible spontaneous products Activity Duration 8h: 4 hours for collecting materials + 4 hours to cook Group Size 5-13 youngsters
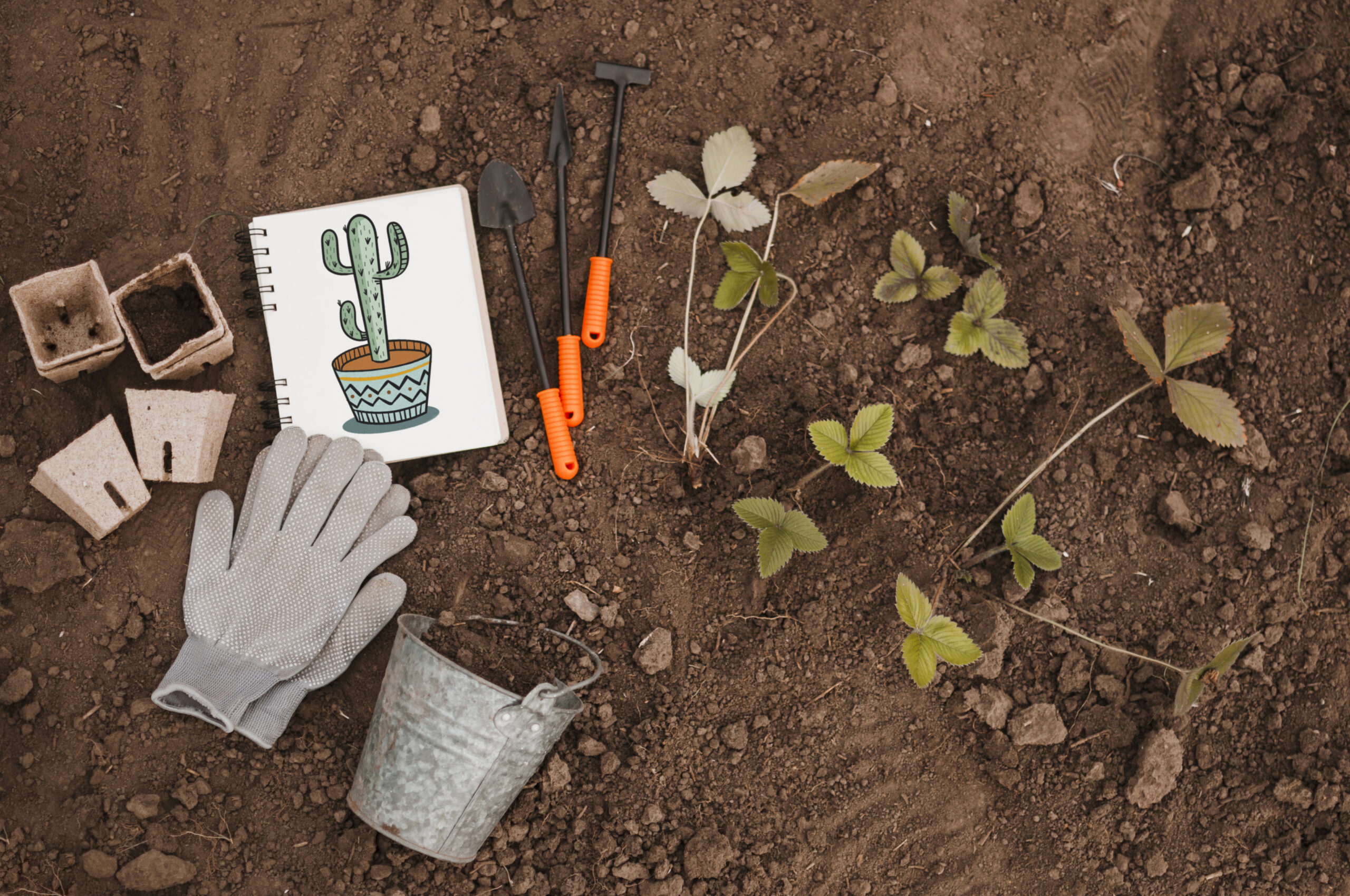

Theme Soil Science, Biodiversity, Regenerative Gardening Activity Duration 1,5 to 2 hours Group Size 4–15 participants (pairs or small teams ideal) Objectives Introduce youth to
Theme Future outlook on climate change Activity Duration 1,5 to 2 hours Group Size 15-25 youngsters Objectives The working method has the following learning objectives:

Theme Energy Activity Duration 3,5 hours Group Size 8-20 youngsters Objectives • Understand the principles of different energy sources (renewable and non-renewable). • Analyse the

Theme Fast fashion Activity Duration 3 hours Group Size 10-20 youngsters Objectives Identify, learn and apply creative and artistic modes of expression to reframe one’s

Theme A positive, sustainable future! Activity Duration 4 – 8 hours Group Size 15 – 25 students Objectives In the process, students develop an answer

Theme Introduction to Permaculture, Ethics, Regenerative Thinking Activity Duration 1.5 hours Group Size 5–20 young people Objectives Introduce the three ethics of permaculture in a

Theme Natural Systems, Observation, Permaculture Design Thinking Activity Duration 1.5 – 2 hours Group Size 4–20 participants Objectives Introduce youth to the concept of natural

Theme Systems Thinking, Sustainability Awareness, Lifestyle Reflection Activity Duration 1.5 hours Group Size Individual or small group (can be shared afterward in groups of 2–4)

Theme Waste Awareness, Circular Economy, Critical Consumption Activity Duration 1.5–2 hours Group Size 4–20 participants Objectives Build awareness of local waste patterns and consumption habits

Theme Ecological Design, Food Sovereignty, Biodiversity Activity Duration 2 hours (can be extended across multiple sessions) Group Size Individual, pairs, or design teams (3–4 participants)

Theme Ecosystems, Interconnection, Systems Thinking Activity Duration 1.5 hours Group Size 6–20 participants Objectives Embody ecological roles to explore natural interdependence Understand how systems respond
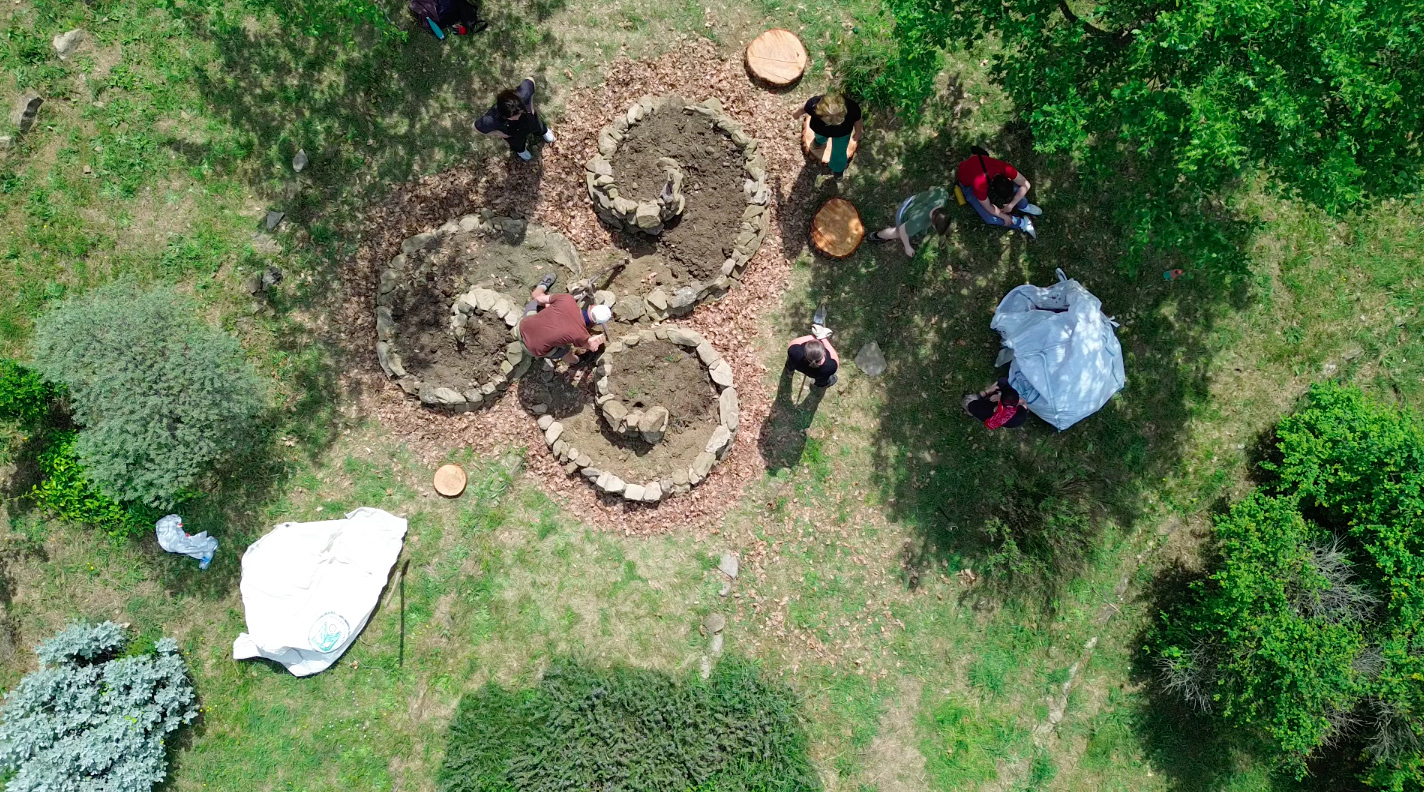

Theme Sustainability Principles, Regenerative Design, Action Learning Activity Duration 1.5–2 hours Group Size 4–25 participants (teams of 2–5) Objectives Deepen understanding of the 12 permaculture
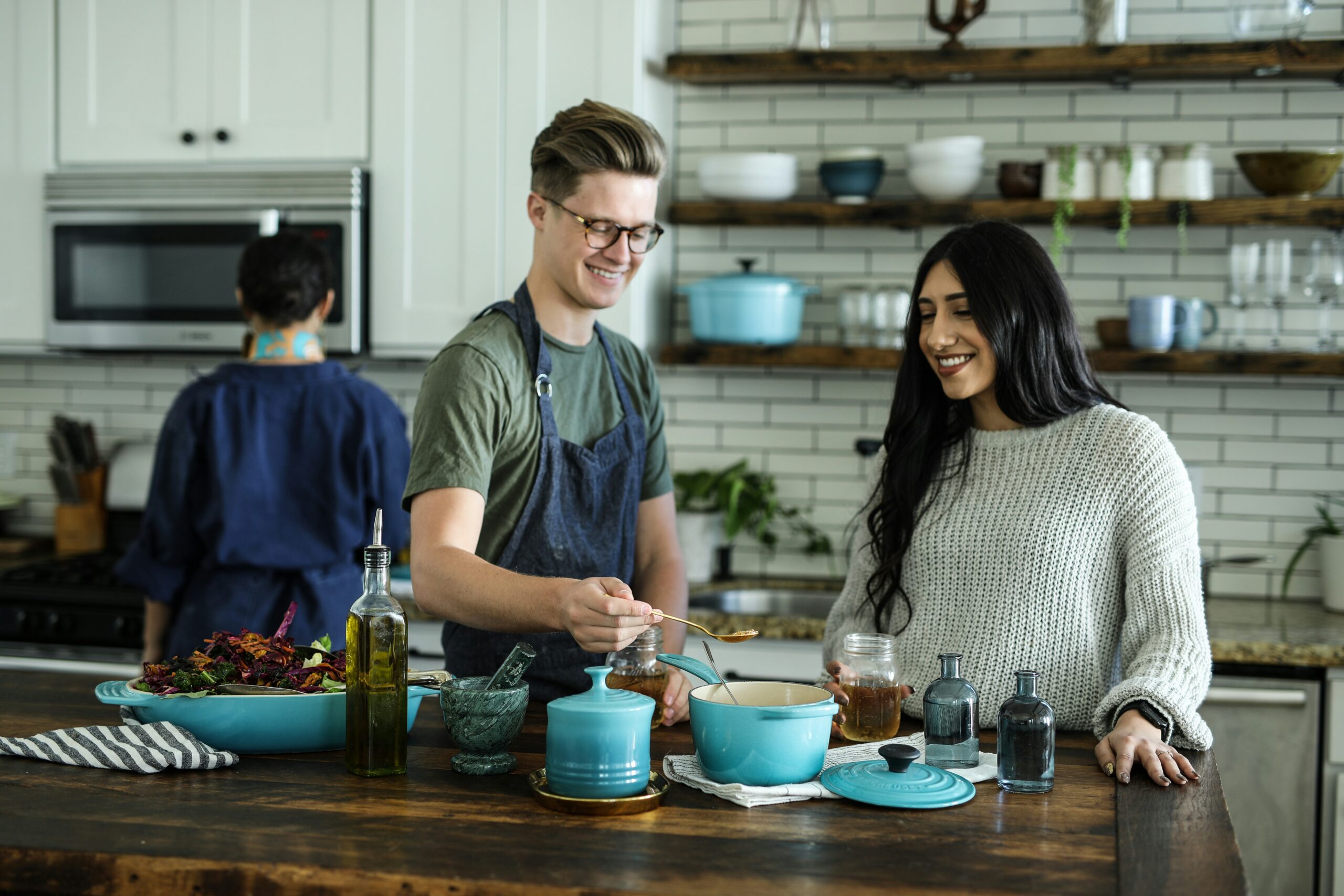

Theme Dutch Cuisine Principle 2 Activity Duration 2 hours Group Size 4-6 in a group Objectives • Gaining insight into a healthy plant-based diet •
©All rights reserved Sustainable Learning 2026